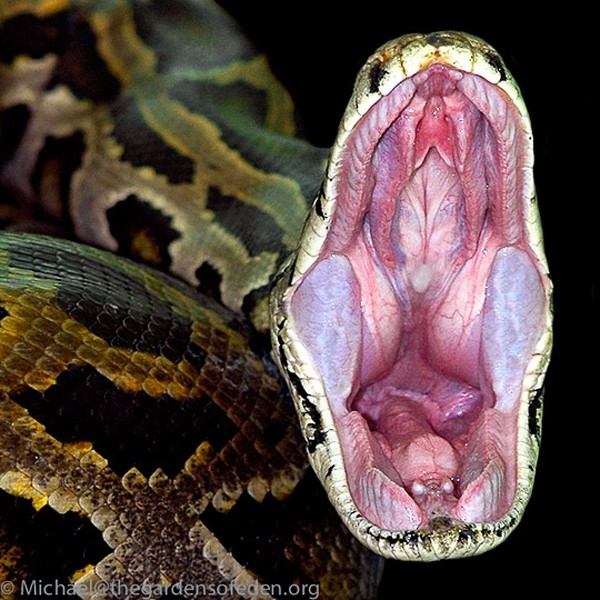
The giant python is a scary and challenging animal. They are commonly found in tropical and subtropical areas, but where they live most often is in South America.
Among the giant pythons, the Anaconda is the best known. They can grow up to 30 feet long and weigh up to 550 pounds. They live in wet forests, large rivers and ponds.

The giant python is known to be one of the largest carnivores on earth. They can eat large animals such as giraffes, cows and even humans.
Although they are carnivores, giant pythons are also an important part of the ecosystem. They help control the numbers of other animals, especially herbivores.

However, the giant python is also a fearsome animal and can be dangerous to humans if left unattended. They can attack humans if they feel threatened or irritated.
In South America, giant pythons have caused many accidents and attacks on people. However, environmental protection measures and education programs have helped to reduce encroachment on their habitats and increase awareness of their importance in the ecosystem.

In short, the giant python in South America is a special animal and plays an important role in the ecosystem. However, they can also be dangerous to humans if left unattended. Therefore, proper supervision and management is required to ensure their existence and ensure human safety.